FAQs
Share
What’s the difference between a hospital inpatient department and a hospital outpatient department?
A hospital inpatient department is the part of a hospital designed for people who visit a hospital for a treatment or procedure that requires at least one overnight stay. Examples of inpatient departments include labor and delivery units for mothers delivering newborns, critical care units for extremely sick patients requiring special intensive care, medical units for patients receiving medical treatment and nursing care, and surgical units for patients recovering from a major surgery.
A hospital outpatient department is the part of a hospital designed for people who visit a hospital for a treatment or procedure that does not require an overnight stay. Hospital outpatient departments may be in a hospital or in a separate building near a hospital and include free-standing surgery centers. Many elective outpatient surgeries are done in hospital outpatient departments.
What’s the difference between a hospital outpatient department and an ambulatory surgery center?
An ambulatory surgery center, also known as an ASC or surgery center, is a distinct entity that exclusively provides elective outpatient surgical services to patients not requiring an overnight stay in a hospital. Important characteristics of surgery centers include the following:
-
Provides surgical services that cannot exceed 24 hours or require an overnight stay in a hospital
-
Often owned by physicians or a joint partnership between physicians and a management company or local hospital
-
Often focused on specific surgical specialties such as orthopedics (bones and joints) or ophthalmology (eyes)
A hospital outpatient department (HOPD) is not a distinct entity; it operates under the license of a hospital. Important characteristics of HOPDs include the following:
-
Provides surgical services that do not require an overnight stay in a hospital
-
Provides outpatient hospital services, meaning preventive, diagnostic, therapeutic, rehabilitative, or palliative services that are furnished to outpatients
-
May be co-located with a hospital (e.g., a unit within the building or building connected to the main hospital) or separately located (e.g., a free-standing surgical center)
What’s the difference between complex and elective outpatient surgery?
Complex surgery, also known as high-risk or major surgery, includes any invasive operative procedures that are typically performed in a hospital and require at least one overnight stay. Complex surgeries can result in dangerous complications and even death.
Elective outpatient surgery, also known as same-day surgery, does not require an overnight stay in a hospital. Elective outpatient surgeries range from cataract surgery to total joint replacements, and also carry some risk. They are often performed in hospital outpatient departments or ambulatory surgery centers and account for the majority of surgeries performed in the U.S.
Does the “volume of procedures” indicate how many surgeries a hospital or surgeon has performed?
Yes. Volume of procedures is the number of times a hospital or surgeon has done a specific surgical procedure in a defined time period (i.e. one year).
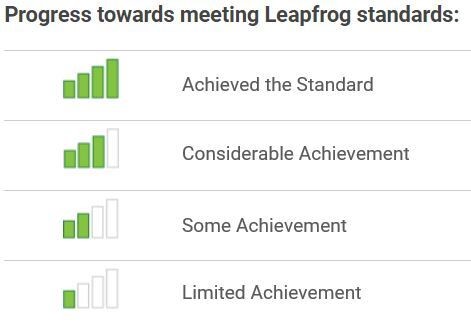
What are "Leapfrog Standards?"
The Leapfrog Group, advised by national experts, sets targets for hospital and surgery center performance for each measure of the Leapfrog Hospital Survey and Leapfrog ASC Survey. Standards help healthcare organizations participating in the Surveys and healthcare consumers identify top performance for patient safety and quality.
Leapfrog uses cell-phone bar icons to communicate a hospital or surgery center’s progress in meeting our standards: